NOAA Study Says: Warming Ocean May Bring Major Changes to Northeast Fisheries
February 11, 2016
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) scientists recently released the first multi-species assessment of just how vulnerable U.S. marine fish and invertebrate species are to the effects of climate change.
The study examined 82 species off the Northeast coast, where ocean warming is occurring rapidly. Researchers found that most species evaluated will be affected, and that some are likely to be more resilient to changing ocean conditions than others.
“Our method identifies specific attributes that influence marine fish and invertebrate resilience to the effects of a warming ocean and characterizes risks posed to individual species,” said Jon Hare, a fisheries oceanographer at NOAA Fisheries’ Northeast Fisheries Science Center in Narragansett, R.I., and lead author of the study. “This work will help us better account for the effects of warming waters on our fishery species in stock assessments and when developing fishery management measures.”
The study is formally known as the “Northeast Climate Vulnerability Assessment” and is the first in a series of similar evaluations planned for fishery species in other U.S. regions. Conducting climate change-vulnerability assessments of U.S. fisheries is a priority action for NOAA.
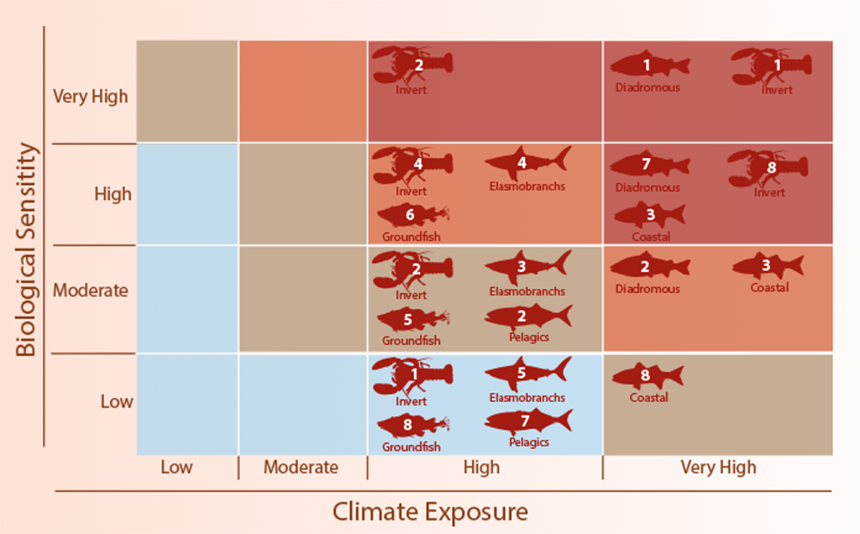
The 82 Northeast marine species evaluated include all commercially managed fish and invertebrate species in the region, a large number of recreational fish species, all fish species listed or under consideration for listing on the federal Endangered Species Act, and a range of ecologically important species.
NOAA researchers, along with colleagues at the University of Colorado, worked together on the project. Scientists provided climate model predictions of how conditions in the region’s marine environment are predicted to change in the 21st century. The method for assessing vulnerability was adapted for marine species from similar work by the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service to characterize the vulnerability of wildlife species to climate change.
The method tends to categorize species that are “generalists” as less vulnerable to climate change than are those that are “specialists.” For example, Atlantic cod and yellowtail flounder are more generalists, since they can use a variety of prey and habitat, and are ranked as only moderately vulnerable to climate change.
The Atlantic sea scallop is more of a specialist, with limited mobility and high sensitivity to the ocean acidification that will be more pronounced as water temperatures warm. Thus, sea scallops have a high vulnerability ranking.
The method also evaluates the potential for shifts in distribution and stock productivity, and estimates whether climate-change effects will be more negative or more positive for a particular species.
“Vulnerability assessments provide a framework for evaluating climate impacts over a broad range of species by combining expert opinion with what we know about that species, in terms of the quantity and the quality of data,” Hare said. “This assessment helps us evaluate the relative sensitivity of a species to the effects of climate change. It does not, however, provide a way to estimate the pace, scale or magnitude of change at the species level.”
Researchers used existing information on climate and ocean conditions, species distributions and life history characteristics to estimate each species’ overall vulnerability to climate-related changes in the region. Vulnerability is defined as the risk of change in abundance or productivity resulting from climate change and variability, with relative rankings based on a combination of a species exposure to climate change and a species’ sensitivity to climate change.
Each species was evaluated and ranked in one of four vulnerability categories: low, moderate, high and very high. Animals that migrate between fresh and salt water, such as sturgeon and salmon, and those that live on the ocean bottom, such as scallops, lobsters and clams, are the most vulnerable to climate effects in the region.
Species that live nearer to the water’s surface, such as herring and mackerel, are the least vulnerable. Most species also are likely to change their distribution in response to climate change, according to the study. Numerous distribution shifts have already been documented, and the study demonstrates that widespread distribution shifts are likely to continue for the foreseeable future.
Categories
Join the Discussion
View CommentsYour support keeps our reporters on the environmental beat.
Reader support is at the core of our nonprofit news model. Together, we can keep the environment in the headlines.
We use cookies to improve your experience and deliver personalized content. View Cookie Settings



